Abstract of the full article available here:
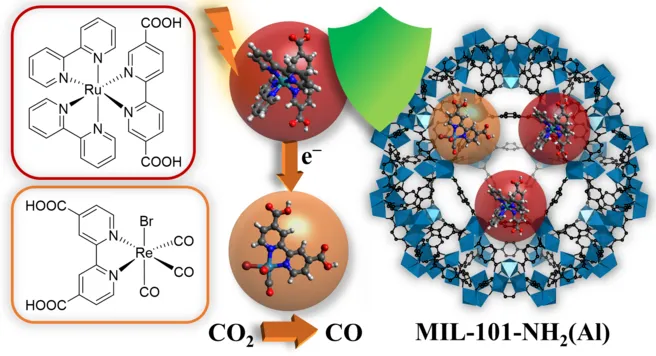
Herein, we report on a molecular catalyst embedding metal–organic framework (MOF) that enables enhanced photocatalytic CO2 reduction activity. A benchmark photocatalyst fac-ReBr(CO)3(4,4′-dcbpy) (dcbpy = dicarboxy-2,2′-bipyridine) and photosensitizer Ru(bpy)2(5,5′-dcbpy)Cl2 (bpy = 2,2′-bipyridine) were synergistically entrapped inside the cages of the nontoxic and inexpensive MIL-101-NH2(Al) through noncovalent host–guest interactions. The heterogeneous material improved Re catalyst stabilization under photocatalytic CO2 reduction conditions as selective CO evolution was prolonged from 1.5 to 40 h compared to the MOF-free photosystem upon reactivation with additional photosensitizer. By varying ratios of immobilized catalyst to photosensitizer, we demonstrated and evaluated the effect of reaction environment modulation in defined MOF cages acting as a nanoreactor. This illustrated the optimal efficiency for two photosensitizers and one catalyst per cage and further led to the determination of ad hoc relationships between molecular complex size, MOF pore windows, and number of hostable molecules per cage. Differing from typical homogeneous systems, photosensitizer—and not catalyst—degradation was identified as a major performance-limiting factor, providing a future route to higher turnover numbers via a rational choice of parameters.