Characterization and validation of screening methods for culture-independent detection of Legionella pneumophila in artificial water systems
OBJECTIVE
For the detection of Legionella contamination in cooling towers, evaporation coolers and wet separators, the industry is searching for culture-independent screening and detection methods. As the gold standard the cultivation method needs 7 - 10 days with unspecific detection of Legionella spp. Furthermore, the slow growth rate supports overgrowing with accompanying flora and can’t describe the current status of such artificial water systems. This project focuses on the characterization and validation of in our institute developed and commercially available molecular biological and antibody based methods for the detection of Legionella pneumophila by analyzing artificial water samples. The main objects are:
- Combination of MAF with CL-SMIA for culture-independent detection and serotyping
- Development of a novel CL-SMIA chip for Sg 2 - 15 detection
- Evaluation of immunomagnetic separation (IMS) kits coupled with flow cytometry
- Evaluation of commercial qPCR kits for L. pneumophila detection with viability function
METHODS
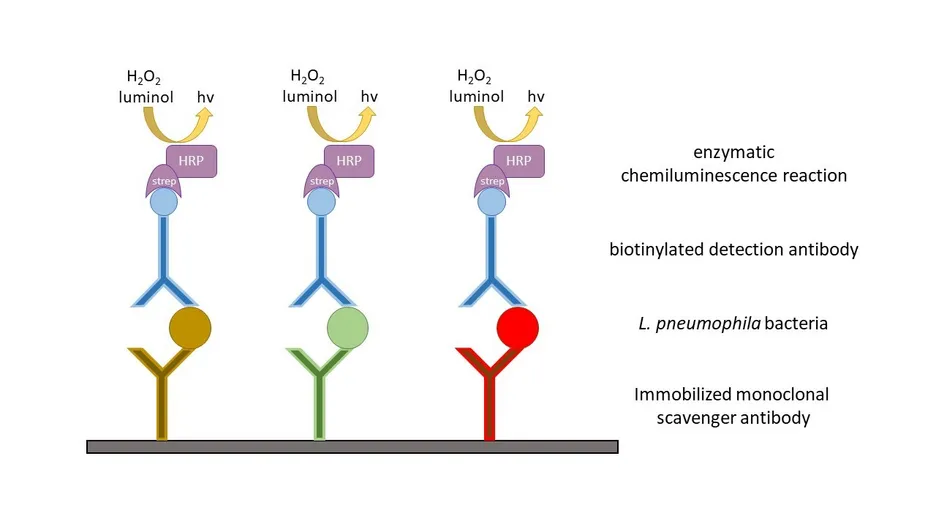
Our institute developed the chemiluminescence sandwich microarray immunoassay (CL-SMIA) which is an antibody dependent screening method and is performed on the Microarray-Chip-Reader-Research (MCR-R) device. The CL-SMIA uses polycarbonate chips coated with several monoclonal antibodies as scavenger antibodies. The sample runs with a slow flow rate (1.0 µL/s) over the chip, that the Legionella can bind onto the chip. The bacteria own lipopolysaccharide chains (LPS) on their membrane, which act as antigens and are recognized by the antibodies. The LPS structures distinguish between each serogroup (Sg) and subgroup, wherefore a simultaneous detection and characterization is possible. The last step of the assay is the chemiluminescence reaction. Biotinylated detection antibody is directed over the chip and sets down on the scavenged Legionella. Afterwards, streptavidin conjugated with several horseradish peroxidase enzymes binds to the detection antibody and the enzymes catalyse the chemiluminescence reaction of luminol and hydrogen peroxide, which can be detected with a CCD-camera. For culture-independent utilization the sensitivity of the assay must be improved by combining the CL-SMIA with monolithic absorption filtration (MAF) as a suitable enrichment method for Legionella.
INVOLVED PHD STUDENTS
M. Sc. Philipp Streich
PARTNERS
Verein Deutscher Ingenieure (VDI) e.V.
GWK Präzisionstechnik GmbH
Bayerisches Landesamt für Gesundheit und Lebensmittelsicherheit (LGL)
Institute of Virology, Medical Faculty, TU Dresden (Prof. Dr. Lück)
Associated Partners
Analytik Jena AG
Aqua-Concept
Endress+Hauser
rqMicro
FINANCIAL SUPPORT
BMWE WIPANO-LegioRapid: FKZ 03TN0002A
www.legiorapid.de